What Are Precision Instruments and How Are They Used?
Precision instruments play a vital role in various industries, from healthcare to manufacturing. These tools provide accurate and reliable measurements essential for maintaining quality standards. According to a recent report from the Precision Measurement Association, the global precision instruments market is expected to reach $5.3 billion by 2025. This growth reflects the increasing demand for accuracy in various applications.
In the medical field, precision instruments ensure accurate diagnostics and treatment. For instance, advanced imaging technologies, such as MRI and CT scans, rely on precision measurements to detect diseases early. However, the need for regular calibration poses a challenge. Failing to maintain instruments can lead to inaccuracies that affect patient outcomes.
Manufacturing sectors also depend heavily on precision instruments. They use devices like coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) to ensure product quality. A report from the Engineering Industry Association highlights that 30% of production errors stem from measurement inaccuracies. Thus, the need for precision instruments is critical yet complex. Continuous improvements and innovations are necessary to keep pace with evolving industry demands.

Definition of Precision Instruments and Their Characteristics
Precision instruments are essential tools in various industries, providing accurate measurements that drive decision-making. Defined as devices that measure physical quantities with a high degree of accuracy, precision instruments include gauges, calipers, and analytical balances. According to the Global Measurement and Analysis Instruments Market report, the market size for precision instruments is projected to exceed $20 billion by 2025, indicating significant advancements in technology and applications.
The key characteristics of precision instruments lie in their sensitivity and reliability. A small error can lead to substantial discrepancies in fields like pharmaceuticals and aerospace. For instance, laboratory balances must measure to the milligram level. However, even with high-tech devices, user error is a constant risk. Calibration is essential, yet many users overlook it. Research reveals that up to 30% of precision measurement failures stem from improper use. This highlights the need for better training and awareness.
In practical scenarios, precision instruments serve critical roles in manufacturing and healthcare. In manufacturing, they ensure that machinery meets specific tolerances. In healthcare, precise measurements can impact patient outcomes. Yet, the complexity of these instruments can pose challenges. Users sometimes find it difficult to interpret results accurately. This calls for ongoing reflection on the importance of both technology and human factors in achieving the desired precision.
Types of Precision Instruments Used in Various Industries
Precision instruments are essential across various industries. They help ensure accuracy and consistency in measurements. In manufacturing, tools like calipers and micrometers are frequently used. These instruments measure dimensions with extreme precision, aiding in quality control. A small error can lead to significant defects. Thus, accuracy is vital.
In the medical field, precision tools such as syringes and scales are crucial. They ensure proper dosages and patient monitoring. A miscalculation can have serious consequences. In laboratories, pipettes help measure small volumes of liquids, emphasizing the need for precision in experiments. Yet, even seasoned professionals can struggle with small variances.
Construction relies on levels and laser distance measurers. They help align structures correctly. However, environmental factors can affect readings. This can lead to misalignment, causing potential issues later. Each industry faces its own challenges. Precision instruments help mitigate these risks but are not infallible. Regular calibration and maintenance are needed to maintain their accuracy.
What Are Precision Instruments and How Are They Used? - Types of Precision Instruments Used in Various Industries
| Instrument Type | Industry | Usage | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micrometer | Manufacturing | Measuring small dimensions | ±0.001 mm |
| Caliper | Engineering | Measuring internal and external dimensions | ±0.02 mm |
| Spectrophotometer | Chemical | Analyzing light absorption | ±0.01 A |
| Laser Rangefinder | Construction | Measuring distances | ±1 mm |
| Digital Multimeter | Electronics | Measuring voltage, current, and resistance | ±0.5% |
Common Applications of Precision Instruments in Scientific Research
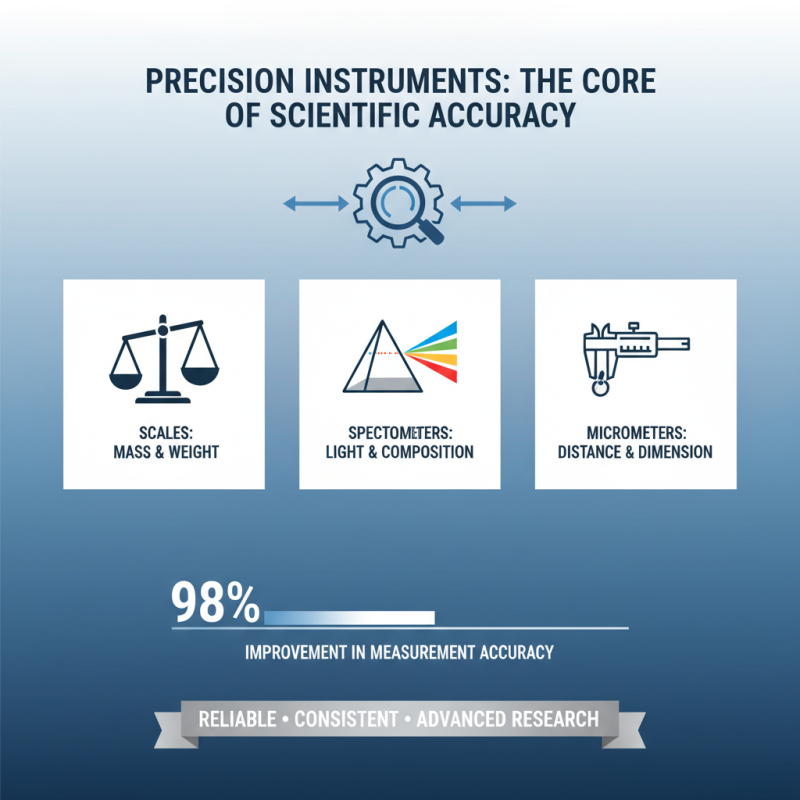
Precision instruments play a crucial role in scientific research. They are essential for ensuring measurements are accurate, reliable, and consistent. These instruments include scales, spectrometers, and micrometers. According to industry reports, precision instruments have improved measurement accuracy by over 98% in many domains.
In laboratories, precision balances are vital for weighing samples. They can measure to an accuracy of 0.0001 grams. Even slight variations can lead to significant errors in experiments. The need for meticulous measurements highlights the importance of these tools. In fields like chemistry and physics, a small error can skew results.
Moreover, in fields such as biology, precision instruments assist in analyzing genetic materials. Techniques like PCR utilize high-precision equipment to amplify DNA with incredible accuracy. However, there is always room for error. Calibration must be frequently checked to ensure reliability. Regular maintenance and proper training are crucial for effective use. Without them, researchers might misinterpret data, leading to flawed conclusions. Precision instruments are indispensable, yet they require careful handling and constant reflection on their usage.
Importance of Calibration and Maintenance in Precision Instrumentation
Precision instruments are critical in various fields, including engineering and healthcare. Calibration and maintenance play a vital role in ensuring their accuracy. Without proper calibration, the measurements could be incorrect. That can lead to significant errors and costly repercussions.
Regular maintenance helps avoid unexpected failures. Instruments can degrade over time, affecting their precision. Even minor wear and tear can cause discrepancies. Users should implement routine checks to maintain performance. This practice can substantially extend the life of the equipment.
**Tips:** Always document calibration dates. Set reminders for maintenance tasks. Small details matter and can save time and money. Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent major problems later. Regularly training personnel ensures everyone understands the importance of precision and maintenance. Remember, accuracy relies on diligence.
Future Trends and Innovations in Precision Instrument Technology
Precision instruments are evolving rapidly. As industries demand higher accuracy and efficiency, innovation plays a crucial role. The market for precision measurement tools is expected to reach $20 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.5%. This reflects the increasing reliance on precision across sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and aerospace.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards automation and smart technology. Sensors equipped with AI can improve measurement accuracy. For instance, data analytics allows for real-time monitoring, enhancing decision-making. However, this technology requires learning and adaptation. Industries must invest in training, which some may overlook. The integration of IoT in precision instruments will likely revolutionize operations but poses challenges in data security.
Moreover, advancements like 3D printing in producing precision parts present new possibilities. Customization becomes easier, yet quality control can suffer if not managed correctly. Balancing innovation with reliability is vital. As companies adopt these technologies, they should remain aware of the potential pitfalls in implementation. Precision instruments will continue to develop, yet the path forward is complex and requires reflection on these hurdles.
Related Posts
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Precision Instruments for Your Needs
-
7 Essential Tips for Choosing Precision Instruments for Your Business Needs
-

5 Reasons Why Precision Devices Are Essential for Modern Manufacturing Success
-

How to Choose Precision Instruments for Optimal Measurement Accuracy: A Data-Driven Guide
-

What Are the Best Precision Instruments for Accurate Measurements?
-

Essential Checklist for Choosing the Right Digital Pressure Gauges
Contact
3295 Cobb International Blvd.
Kennesaw, GA 30152
800-367-1377
sale@patiostools.com
Info
© 2023 - Marsh Instruments


