What is a Test Gauge and How Does It Work in Measurement Applications
Test gauges play a crucial role in various measurement applications, providing precise and reliable data for both industrial and scientific purposes. These devices are designed to assess and calibrate different parameters, such as pressure, temperature, and mechanical aspects of materials, ensuring that measurements meet established standards. Understanding how test gauges function not only enhances the accuracy of measurements but also contributes to the overall efficiency and safety of operations.
In practice, test gauges serve as vital tools across numerous industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and engineering. By utilizing these instruments, professionals can detect discrepancies in measurements, allowing for timely adjustments and improvements. The operation of a test gauge typically involves comparing a measured value against a known standard, ensuring that any variations can be identified and rectified. This process is essential in maintaining quality control and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Moreover, test gauges are not only limited to direct measurement; they often play a significant role in diagnostics and equipment maintenance. By regularly utilizing test gauges, organizations can proactively monitor performance, significantly reducing the risk of failure and enhancing the longevity of their equipment. Thus, a clear understanding of test gauges and their mechanisms offers invaluable insights into their benefits and applications in the field of measurement.

Definition and Purpose of a Test Gauge in Measurement
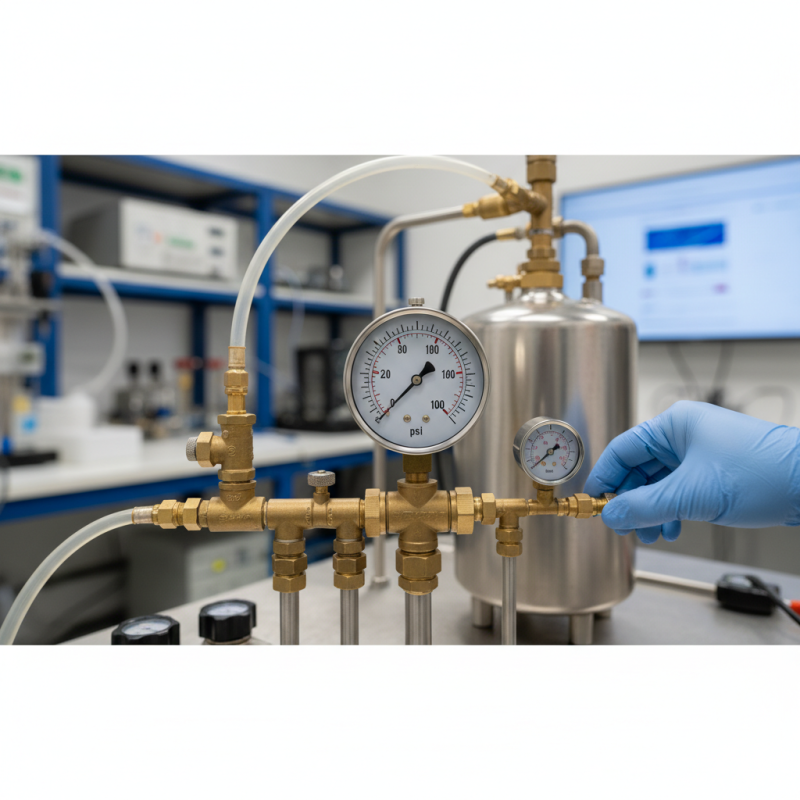
A test gauge is a precision instrument used to measure pressure, temperature, or other specific parameters in various applications. Its primary purpose is to provide an accurate assessment of a system's performance, ensuring that equipment operates within designated safety and efficiency standards. Test gauges are essential in industries such as manufacturing, HVAC, and automotive, where maintaining optimal functioning is critical.
Tips: When selecting a test gauge, consider the specific measurement requirements of your application. Look for gauges with a suitable range, accuracy, and durability to ensure long-term reliability.
The operation of a test gauge typically involves sensing the physical property being measured and converting it into a readable format. For instance, in pressure gauges, a diaphragm or Bourdon tube reacts to changes in pressure, moving a needle on a dial to display the measurement. This functionality allows technicians and engineers to make informed decisions based on the data provided, enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
Tips: Regular calibration and maintenance of test gauges are crucial for accurate measurements. Schedule periodic checks to ensure your instruments are functioning correctly, which helps prevent costly errors in assessments.
Types of Test Gauges Used in Various Industries

Test gauges are crucial tools utilized across various industries to ensure precise measurements and maintain quality standards. Different types of test gauges cater to specific measurement needs depending on the industry. For instance, in the manufacturing sector, dial indicators are commonly employed for measuring linear distances and verifying the precision of machined components. They help engineers and quality control personnel check for variances in dimensions, thereby ensuring that products meet specified tolerances.
In the automotive industry, pressure gauges play a vital role in assessing fluid pressures within systems such as engines and hydraulics. These gauges help technicians monitor performance and detect potential issues early, contributing to vehicle safety and efficiency. Similarly, in the construction field, digital temperature and humidity gauges are used to monitor environmental conditions that can affect material performance and safety during building processes. The diversity of test gauges available reflects the tailored approaches industries adopt to achieve precise, reliable measurements essential for operational success.
Principles of Operation for Accurate Measurement
A test gauge is an essential tool in various measurement applications, designed to provide precise readings of pressure, temperature, or other crucial physical properties. At its core, the principle of operation relies on the interaction between the measuring device and the variable it assesses. For example, in pressure measurement, a test gauge often utilizes a diaphragm that flexes under varying pressure, translating these changes into a readable measurement. The accuracy of these readings is critically dependent on the calibration of the gauge, ensuring that even minute variations are detected.
When utilizing a test gauge, it is essential to be aware of the environmental conditions as they can significantly affect measurement accuracy. Tips for achieving precise measurements include routinely calibrating the gauge according to manufacturer guidelines and selecting a gauge appropriate for the specific application and range of measurement. Additionally, maintaining a stable environment, free of shocks and vibrations, can enhance the reliability of the readings obtained.
Another key aspect of operating a test gauge effectively lies in understanding the significance of fluid dynamics, particularly in liquid or gas environments. Fluctuations in flow and pressure can distort readings. To mitigate this, one should ensure proper installation and alignment of the gauge in the system. It is also advisable to regularly inspect for any wear or damage that could lead to inaccuracies, preserving the integrity of the measurements taken.
Calibration and Maintenance of Test Gauges
Calibration and maintenance of test gauges are crucial for ensuring accurate and reliable measurements across various applications. Calibration refers to the process of comparing a test gauge's output with a known standard to identify any discrepancies. This process not only helps detect errors but also aligns the gauge's reading with industry standards. Regular calibration schedules are essential, as environmental factors, wear and tear, and aging can all impact a gauge’s performance. Establishing a timeline for calibration, including periodic checks based on usage intensity and environmental conditions, helps maintain accuracy.
Maintenance goes hand in hand with calibration to ensure consistent performance of test gauges. This involves routine inspections for any physical damage or signs of wear, such as leaks or corrosion. Proper storage conditions also play a vital role; gauges should be kept in a controlled environment to protect them from humidity, temperature fluctuations, and dust accumulation. Additionally, keeping detailed records of calibration and maintenance activities aids in tracking the gauge's history, which is useful for compliance and quality assurance in measurement applications. Regular attention to both calibration and maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of test gauges and improve the overall reliability of measurement systems.
What is a Test Gauge and How Does It Work in Measurement Applications - Calibration and Maintenance of Test Gauges
| Measurement Application | Test Gauge Type | Calibration Frequency | Maintenance Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Measurement | Digital Pressure Gauge | Annually | Keep clean, calibrate before critical measurements |
| Temperature Measurement | Thermocouple | Semi-Annually | Inspect for wear, ensure proper connection |
| Flow Measurement | Coriolis Flow Meter | Every 6 Months | Clean regularly, check for leaks |
| Dimensional Measurement | Caliper | Annually | Store in protective case, keep clean |
| Voltage Measurement | Digital Multimeter | Quarterly | Check battery life, inspect probes |
Applications and Benefits of Using Test Gauges
Test gauges are essential tools in various industries for accurate measurement and quality assurance. They are utilized to assess the performance of other measuring instruments, ensuring that measurements are consistently reliable. One notable application of test gauges is in the calibration of pressure instruments, which is critical in sectors such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. According to the International Society for Automation, approximately 80% of process safety incidents can be traced back to measurement inaccuracies, underscoring the importance of employing test gauges to maintain precision and safety.
The benefits of using test gauges extend beyond mere compliance with industry standards; they play a vital role in enhancing operational efficiency. For example, their implementation can lead to a reduction in downtime associated with equipment malfunctions. A study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology indicates that accurate measurement practices can increase operational efficiency by up to 20%. Furthermore, test gauges also contribute to cost savings by minimizing waste and preventing product rejections, thus providing a tangible return on investment. By facilitating regular calibration and validation of measurement devices, test gauges ensure that quality remains at the forefront of production processes.
Test Gauge Measurement Applications
This chart illustrates the different measurement applications of test gauges, highlighting their significance in various industries. Each bar represents the number of applications associated with specific measurement types.
Related Posts
-

7 Essential Reasons to Choose the Right Instruments and Gauges for Your Industry
-

Ultimate Guide to Understanding Measuring Instruments for Your Business Success
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Refrigeration Gauges for Your Needs
-

2025 Top 10 Innovations in Pulp and Paper Industry: Transforming Sustainability with 80% Recycled Fiber Usage
-

Navigating the Challenges of Precision Devices in Today's High Demand Markets
-

7 Reasons Why Investing in Test Instruments Can Transform Your Quality Assurance Process
Contact
3295 Cobb International Blvd.
Kennesaw, GA 30152
800-367-1377
sale@patiostools.com
Info
© 2023 - Marsh Instruments


